
But some of the energy is also absorbed by objects, such as the eardrum in Figure 14.5, and some of the energy is converted to thermal energy in the air. The amplitude of a sound wave decreases with distance from its source, because the energy of the wave is spread over a larger and larger area.

For ordinary, everyday sounds, pressures vary only slightly from average atmospheric pressure. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure it is positive for pressures above atmospheric pressure, and negative for pressures below it. The graph shows gauge pressure (P gauge) versus distance x from the source.
Are sound waves larger than light waves series#
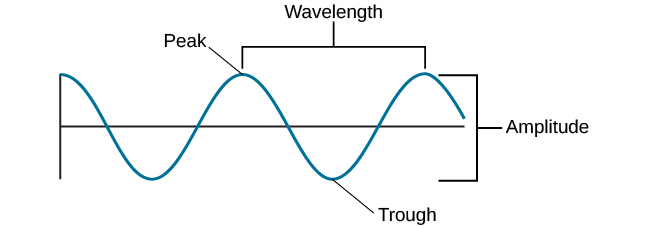
You may recall from the chapter on waves that areas of compression and rarefaction in longitudinal waves (such as sound) are analogous to crests and troughs in transverse waves.įigure 14.4 After many vibrations, there is a series of compressions and rarefactions that have been transmitted from the string as a sound wave. Some of the energy is lost in the form of thermal energy transferred to the air. The pressure disturbance moves through the air as longitudinal waves with the same frequency as the string. regions are compressions, and the low pressure regions are rarefactions. This creates slightly higher and lower pressures. As the string oscillates back and forth, part of the string’s energy goes into compressing and expanding the surrounding air. Some sound waves can be characterized as periodic waves, which means that the atoms that make up the matter experience simple harmonic motion.Ī vibrating string produces a sound wave as illustrated in Figure 14.2, Figure 14.3, and Figure 14.4. A disturbance is anything that is moved from its state of equilibrium. More specifically, sound is defined to be a disturbance of matter that is transmitted from its source outward. Review properties of waves-amplitude, period, frequency, velocity and their inter-relations. Review waves and types of waves-mechanical and non-mechanical, transverse and longitudinal, pulse and periodic.
Are sound waves larger than light waves manual#
In addition, the High School Physics Laboratory Manual addresses content in this section in the lab titled: Waves, as well as the following standards: (F) describe the role of wave characteristics and behaviors in medical and industrial applications.(C) compare characteristics and behaviors of transverse waves, including electromagnetic waves and the electromagnetic spectrum, and characteristics and behaviors of longitudinal waves, including sound waves.

(B) investigate and analyze characteristics of waves, including velocity, frequency, amplitude, and wavelength, and calculate using the relationship between wave speed, frequency, and wavelength.(A) examine and describe oscillatory motion and wave propagation in various types of media.The student knows the characteristics and behavior of waves. The learning objectives in this section will help your students master the following standards:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
